import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
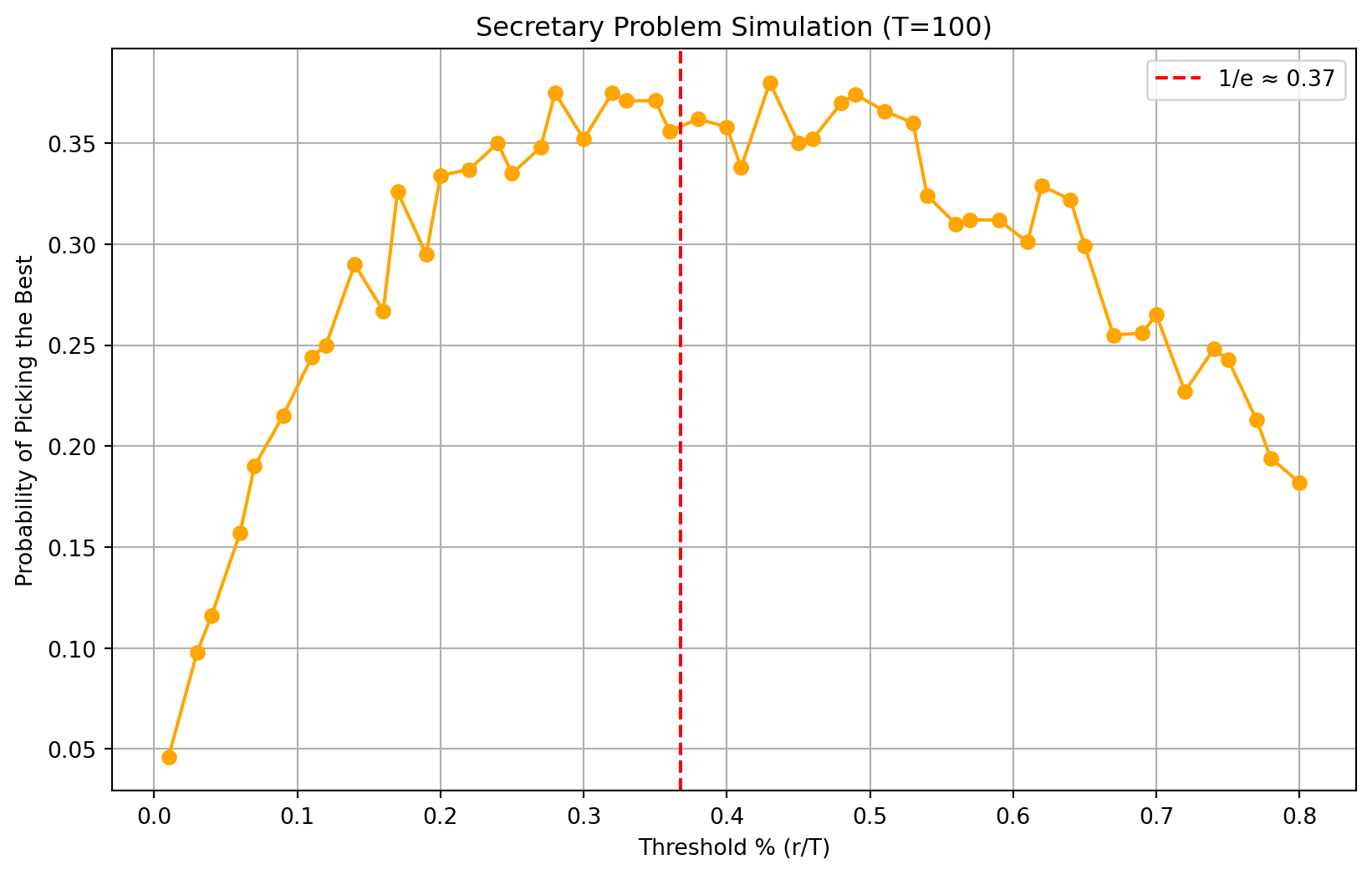
def secretary_simulation(n=100, nmc=1000):
np.random.seed(17)
rules = np.unique(np.round(n * np.linspace(0.01, 0.8, 50)).astype(int))
rules = rules[rules > 0]
success_rate = np.zeros(len(rules))
for i, r in enumerate(rules):
for _ in range(nmc):
candidates = np.random.permutation(np.arange(1, n + 1))
screen = candidates[:r]
best_screen = np.max(screen) if len(screen) > 0 else 0
choices = candidates[r:]
selected = None
for c in choices:
if c > best_screen:
selected = c
break
if selected is None:
selected = candidates[-1]
if selected == n:
success_rate[i] += 1
return rules, success_rate / nmc
rules, prob_best = secretary_simulation()